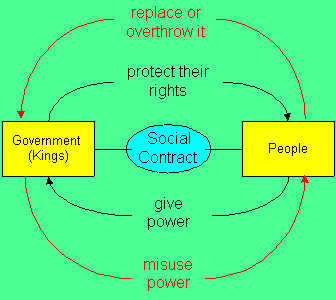
The U.S. Constitution establishes a government based on "federalism," or the sharing of power between the national, and state (and local) governments. Our power-sharing form of government is the opposite of "centralized" governments, such as those in England and France, under which national government maintains total power.
While each of the 50 states has its own constitution, all provisions of state constitutions must comply with the U.S. Constitution. For example, a state constitution cannot deny accused criminals the right to a trial by jury, as assured by the U.S. Constitution's 6th Amendment.
Under the U.S. Constitution, both the national and state governments are granted certain exclusive powers and share other powers.